This is my second post on the Lumix GH7. After discussing in detail autofocus which was for me top priority I want to cover more in detail image quality and ergonomics.
Image Quality
The GH6 was not a step forward in terms of image quality from the GH5M2. I have owned all the models GH5, GH5M2, GH6, GH7 and from a photography point of view the pinnacle has been the GH5M2 which was a more significant step forward from the original model most people think. I have provided test data to photonstophotos for all the follow up models and this graph summarises the situation when it comes to RAW PDR.
What this tells you is that both the GH5M2 and GH7 are a step forward from the original GH5 while the GH6 was an improvement only from ISO 800. Considering that underwater on micro four thirds you will always be shooting ISO 100-200 the GH6 was not really adequate for photo performance. It is true that the GH5 has been really the target of video shooters however GH stands for Hybrid cameras and the series has been made of models that could do very good video and photos. The GH6 was really a video beast the GH7 that has the same body is back on the GH5 tradition of top performing hybrid camera.
A few key improvement over the GH5 include:
- Increased resolution 25 Megapixels vs 20.2
- New RAW files with 16 bits depth
- Dual Gain Output Circuit
- Back illuminated sensor
The GH7 does have some interesting topside features like the ability to record pre-burst images and reach 60 fps with continuous autofocus but those are more for the bird shooter and not applicable to underwater use. Panasonic declares that image quality may drop for shutter speed slower than 1/15 at ISO 100 and therefore this should be your slowest setting also underwater. I do not see this as a limitation even for panning shots.
Many users confuse resolution and megapixels. Spatial resolution is computed on a single dimension in line per millimetre. Therefore the increase in resolution compared to the GH5 and GH5M2 is only 11.4% (5776/5184) this is not exactly life changing but more pixels are always better than less pixels bearing in mind that pixel size and image overall noise are NOT related.
With regards to the dual gain output circuit the increase in peak dynamic range compared to the GH5M2 is only 0.3 Ev (10.17 vs 9.87) and is entirely due to the fact that base sensitivity is now ISO 100 instead of 200.
In the ISO range between 200 and 2500 the GH7 is not better than the GH5M2 and from ISO 3200 it gets better in virtue of noise reduction. Again we are never going to shoot ISO 3200 underwater so this is for us of limited interest.
Perhaps the most interesting feature of the GH7 are the new 16 bits RAW files.
A typical wide angle image has a size of 38 MB which is rather large considering the 25 Megapixels, for reference Sony A7 IV files are around 42 MB. There are several discussion about the efficiency of Panasonic compression but we are not going to go and deep dive on this. What matters to use is how much beating the raw files can take.
Modern cameras exhibit peak dynamic range when underexposed 3 stops from a grey card (I know this sounds strange but is a fact). The way to assess how much beating a file can take is to select one image where your strobe did not fire or was too weak for the situation and increase exposure three stops and see the resulting image.
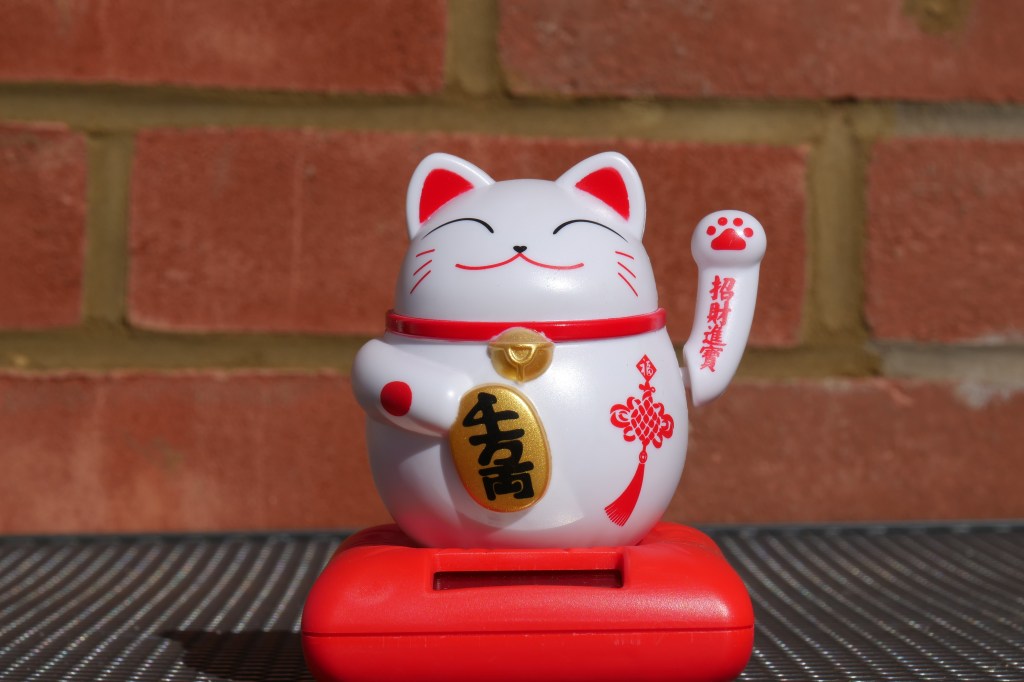
This is an underexposed image as an example where I had forgotten to turn up the strobes.
This is the image applying +3 exposure and other corrections.
The camera can easily take +3 adjustment as well as shadows up to 100% which is an excellent result.
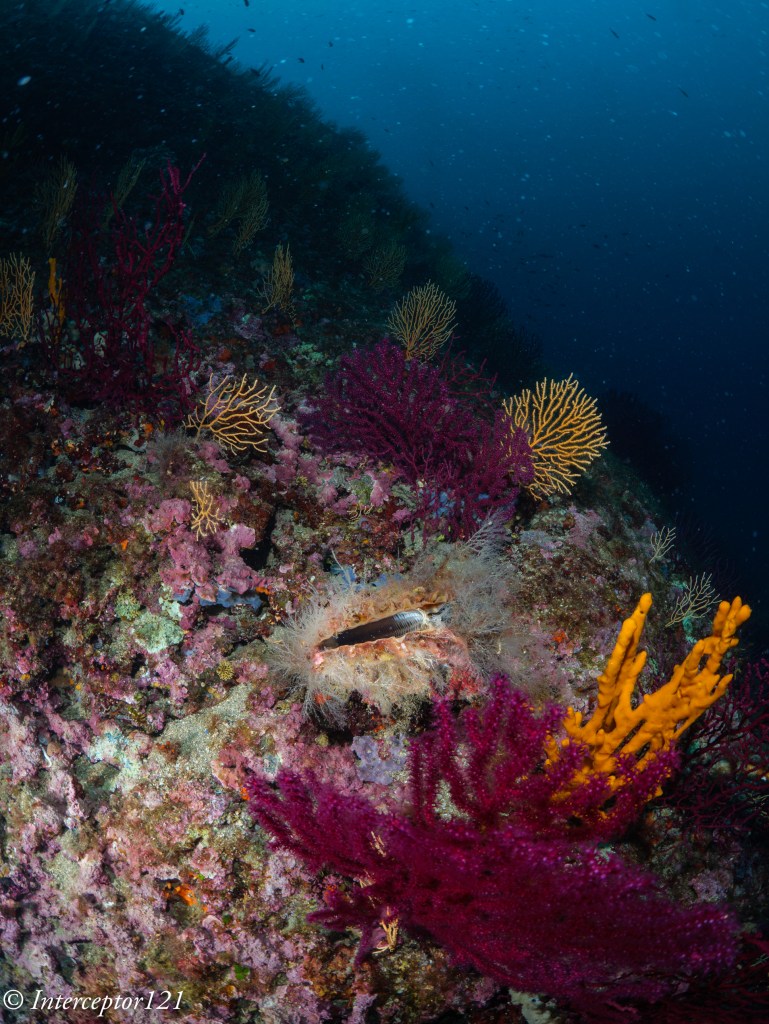
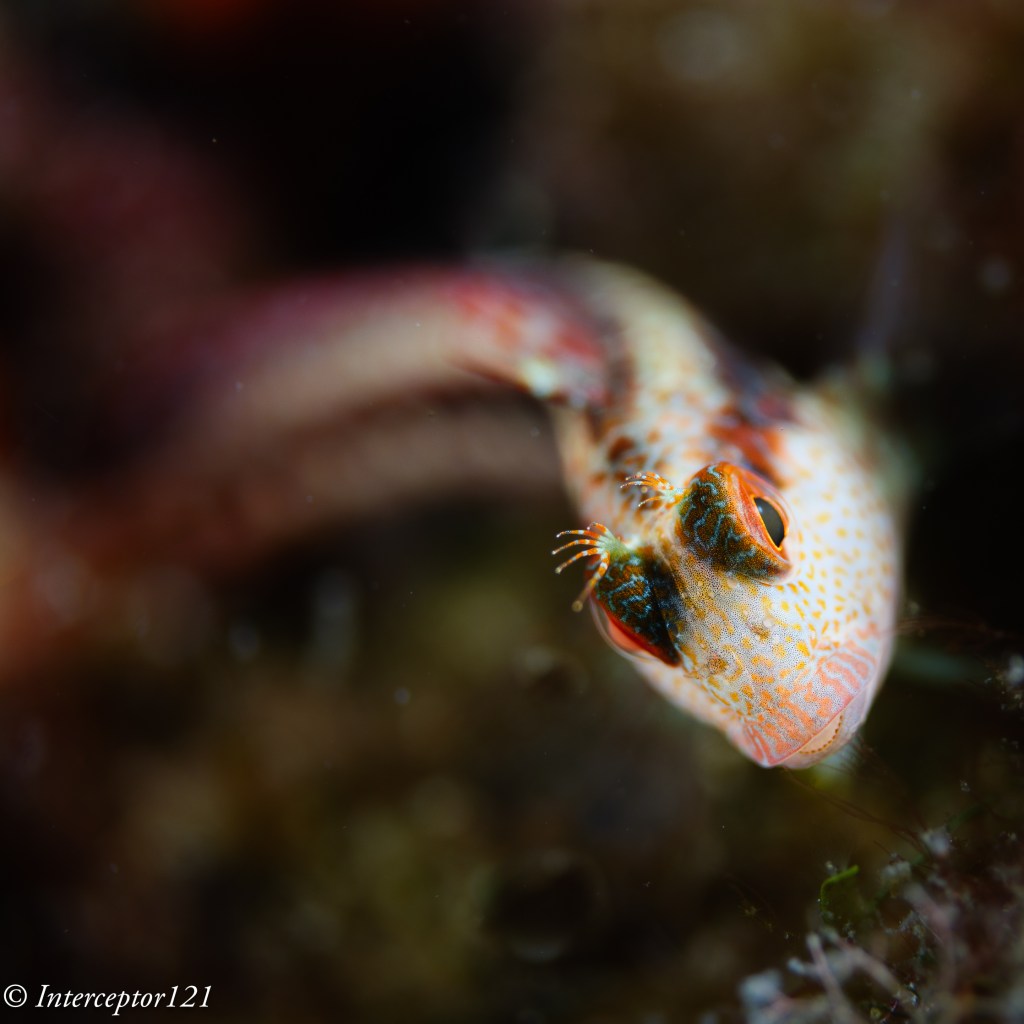
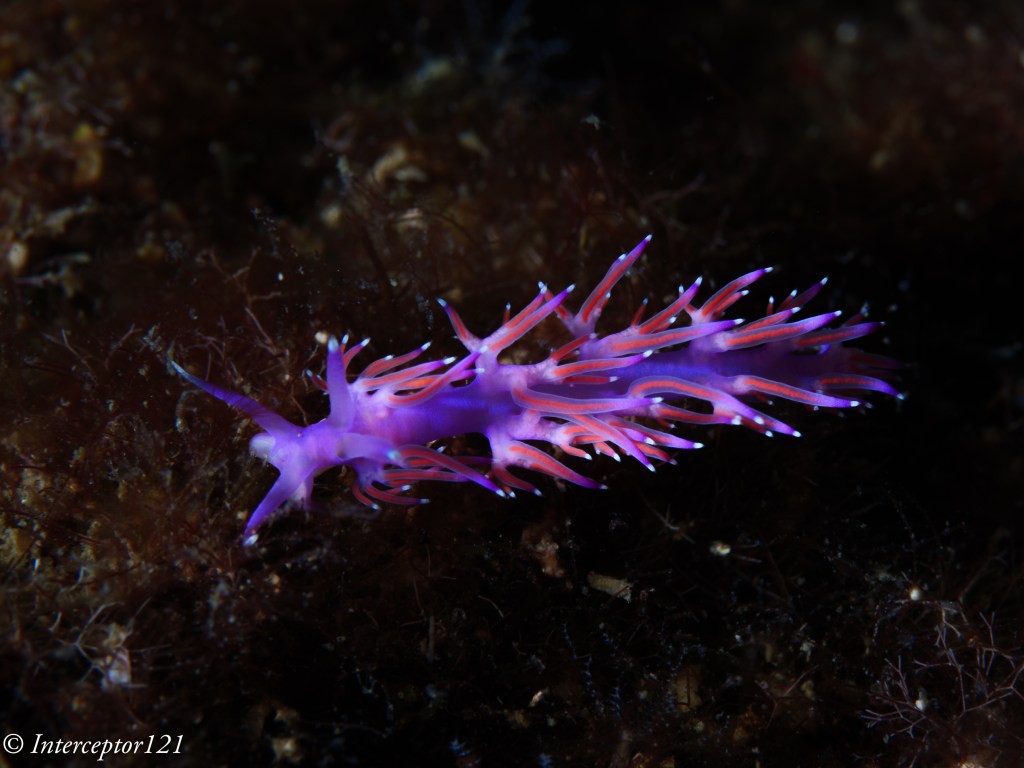
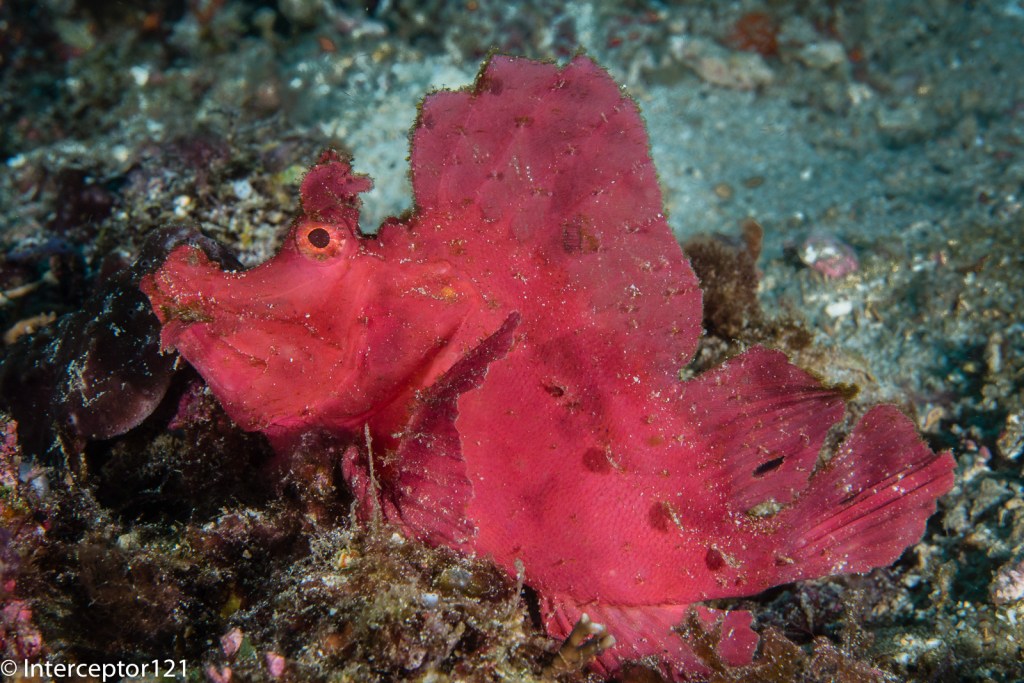
The other aspect of image quality is of course the lens and we can here use the excellent canon 8-15mm in the entire zoom range.
Compared with my A1 in a similar shot I can say that at the edges the GH7 is superior and in the centre the difference in actual resolution is small to non-existent despite half the pixels.
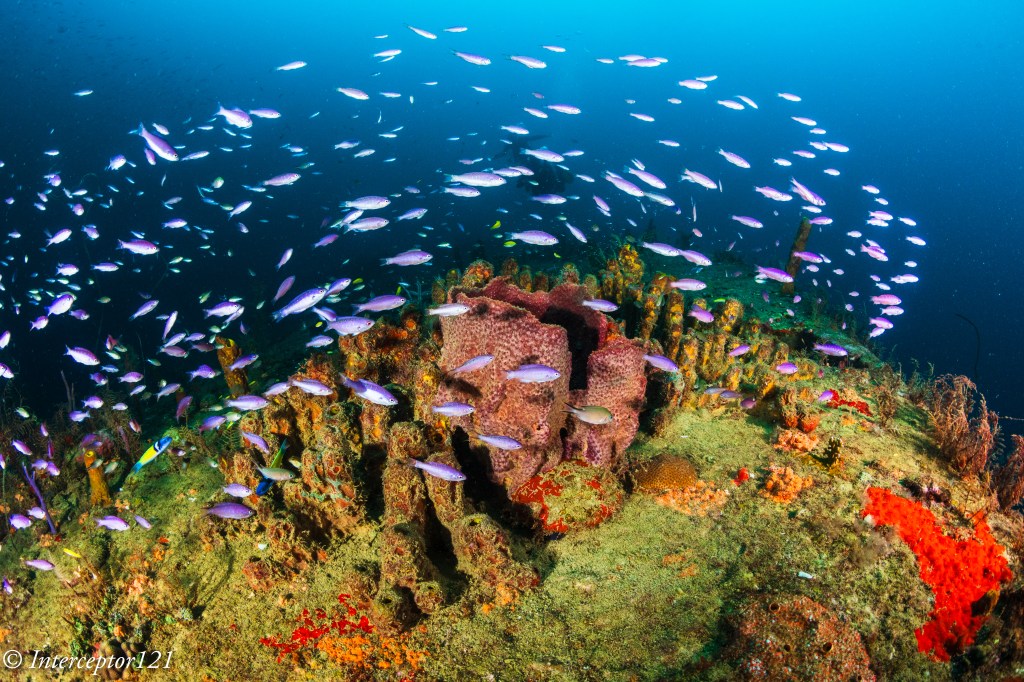


This is because the lens shot at f/16 drops considerably in resolution compared to f/8 which are the equivalent apertures in full frame to micro four thirds. The files are full resolution I let you do the pixel peeping.
This resolution chart shows the underlying reason when the lens goes from f/8 to f/16 looses 30% of the resolution. Taking into account the smaller pixels of the GH7 this could mean an additional drop to the point the images are indeed very similar.
All in all the RAW files of the GH7 can take a lot of beating without issues as long as you do not clip the highlights like any other camera.
In general terms I feel the RAW files of the GH7 are similar in handling to my A1 and A7C II.


Housing Ergonomics
Lets’ first cover the drawbacks of the Nauticam housing.
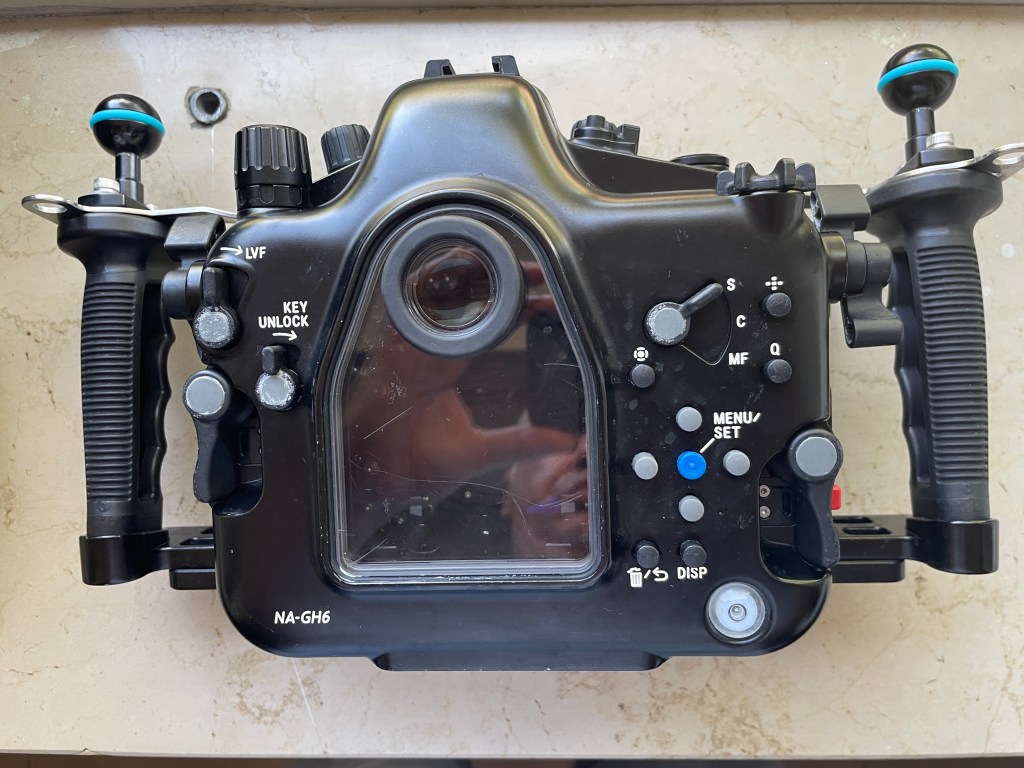
As mentioned in the autofocus post the housing does not give you access to the joystick which is a drawback. There are other two issues with the housing, the handles are angled forward, something typical of the Nauticam GH series that I continue not to understand. Why would the GH5 be any different from other cameras?
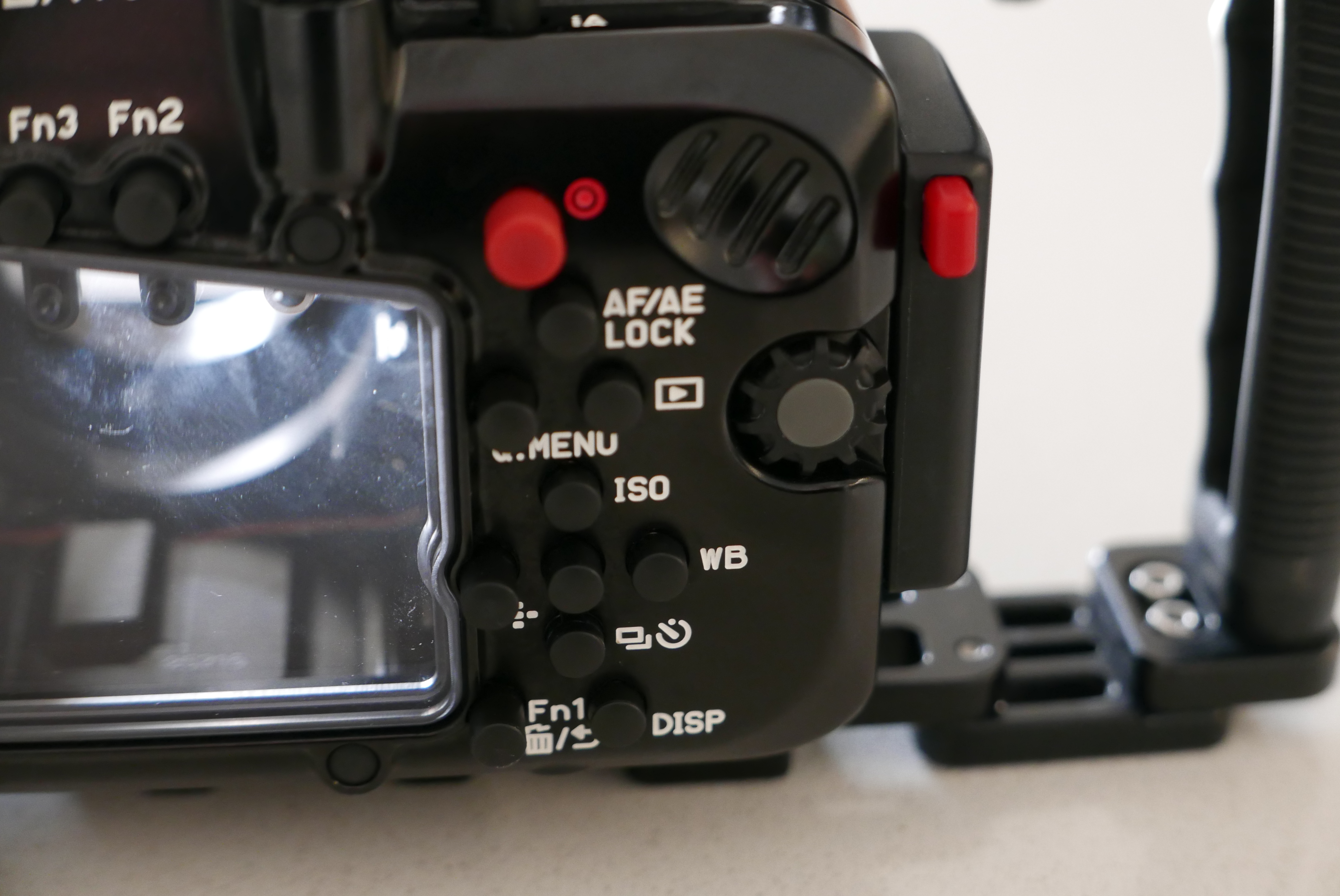
Not all function buttons are accessible in particular the two on the left side of the camera are not. Those are to be fair not the most important buttons and there is already a variety of buttons and controls available so except the joystick there will not be an issue underwater.
The lever under the front ring controls the function buttons 2 and 3 that correspond to the front two buttons of the camera.

I recommend using one for constant preview, hitting will circle through aperture simulation, shutter simulation or nothing and the other can be used to recall the focus limiter which is very important for macro shooting as explained in the previous post. The function button on the back can be your fn 9 to recall the focus area movement useful if you want to move it.
In total you have access to 3 function buttons as well as white balance, ISO, exposure compensation, focus mode, operation lock, EVF/LCD, quick button, menu and the four arrows, delete, mode, shutter mode, playback, movie, af on so there is nothing really missing.

One very important feature is that the handles position can be adjusted, I move out the left handle so that the lens is central to the handles, on my A1 I needed to buy an extension as the port is closer to the left handle.
The housing also has an M10 accessory port as well as the ability to host M5 like the A1, and two ports for monitor and vacuum valve in addition to a cold show
While nauticam recommends the M5 accessory personally I find the cold shoe and especially the M10 port more suitable for focus light and external monitors.
One awkward thing is the N120 to N85 adapter port has the release on the bottom of the camera but that is not a housing issue yet something to bear in mind. The housing is not small at 331x176x136 with a weight of 2.8 kg is indeed similar or equal to a full frame camera.
The final consideration is that the price of the GH6 housing that is compatible with the GH7 is very high, more than a Sony A7 IV, less than Sony A1 and way more than other smaller micro four thirds body as well as other full frame (the S5II housing costs less).
Who is the GH7 for?
The Panasonic GH7 is without a doubt one of the most capable hybrid mirrorless cameras on the market however due to the housing price is unlikely to be attractive to the masses. If you are cost conscious you can get the OM-1 for less due to the smaller housing, if you want performance several full frame cameras will incur similar cost. The real strength of the micro four thirds is the lens choice. You can cover everything with the Canon 8-15 or if you prefer with the Tokina 10-17 there are many wide and macro lenses and the huge depth of field means everything will be consistently sharp across the frame. The real strength of the GH7 though is hybrid use, if you want a camera equally capable of top range photos and videos you are looking at Sony A1 or Nikon Z8 or similar or the GH7 and here it becomes interesting for the latest Panasonic. In the near future I will provide some details of how the GH7 performs as a video capture device.



 [D.FOCUS Movement] / [Fn] / [MENU] / [OFF]
[D.FOCUS Movement] / [Fn] / [MENU] / [OFF]
 . Operations that can be performed by moving the joystick are disabled.
. Operations that can be performed by moving the joystick are disabled.